It can be quite useful to know under which folder path iTunes stores the backup files of iPhone, iPad and Co. These are initially only stored locally on the computer on which iTunes is installed. If this computer then has a defect, the backups may also be lost. If you know where the backups are stored, you can save them as an additional backup on an external drive. Or you want to change the storage location so that the backups are saved on an external drive or a NAS with RAID system.
iTunes and iPhone backup: where are the backups stored?
When using iTunes on a Windows computer to create a backup of the iPhone or iPad, it is stored in an iTunes directory by default. The exact location of the iPhone backup depends on the version of Windows and iTunes that is being used. Here are the default backup directories for different versions of Windows:
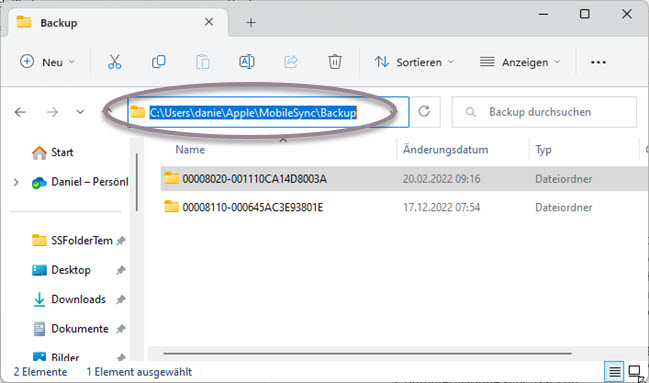
- Windows 11: C:\Users\[Username]\Apple\MobileSync\Backup
- Windows 10: C:\Users\[Username]\Apple\MobileSync\Backup
- Windows 8: C:\Users\[Username]\AppData\Roaming\Apple Computer\MobileSync\Backup
- Windows 7: C:\Users\[Username]\AppData\Roaming\Apple Computer\MobileSync\Backup
Show hidden files
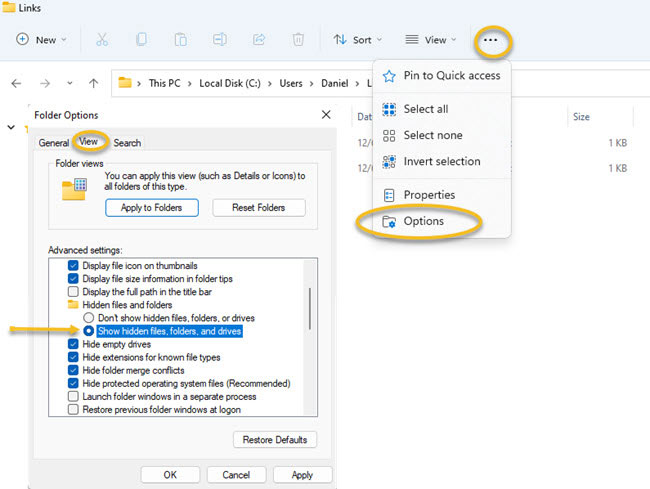
It should be noted that the AppData directory is usually hidden. So you need to enable the “Show hidden files” option in the folder options to see the directory. To enable the “Show hidden files” option, do the following:
Open Windows Explorer and click on the “View” menu. Then click on “Options” and select the “View” tab. Scroll down until you see the “Show hidden files, folders and drives” option and enable it. Finally, click “OK” to save the settings.
Change location for iTunes and iPhone backup
As mentioned above, it can be useful to outsource the backup and store it under a different path, on the one hand to achieve a higher availability or on the other hand to not fill up the local hard disk unnecessarily.
To store the iTunes backup at a different location in the future, you can use the so-called symlink (symbolic link) under Windows. This creates a link to the new location. All storage activities that are then performed on the original path are then written to the referenced directory. Such a symlink can be created under the command line or under PowerShell with the command mklink.
- Call up the Windows Start menu
- type in “CMD“, “Command Prompt” or “PowerShell”
- then right click and select “Run as administrator”
- enter mklink command: mklink C:\Users\Username\Apple\MobileSync\Backup p:\05_DataBackUp\iPhone\
- adjust directory paths, replace username with your own user account and press return
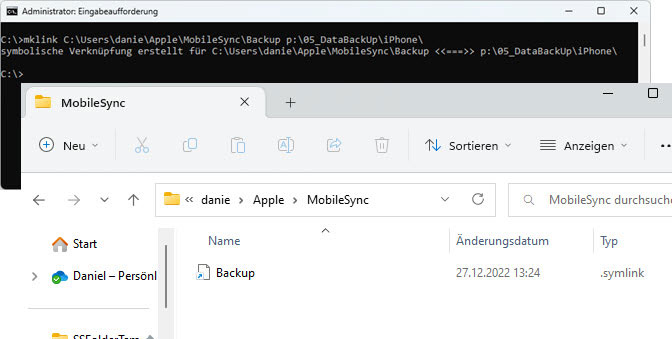
In the picture you can see that instead of the backup folder now a symlink has been created that points to the external directory. If you now run iTunes.exe and start the backup, the backup files are stored in the new external location. The symlink is to be understood as a kind of link and also the symbolism points to it.
Note: If necessary it can come to problems when executing mklink that the access is denied. Possible causes are described in the linked article.

